Java Type Casting
Hello guys and welcome to Code2Night! In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of Java Type Casting. Type casting plays a crucial role in programming as it allows us to convert one data type into another, facilitating compatibility and enabling us to manipulate and utilize our data effectively. Whether you're a beginner seeking a solid foundation in Java or an experienced developer looking to improve your skills, this article will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of typecasting in Java and its practical applications. So, let's dive in and explore the intricacies of Java Type Casting together!
Type casting is when you assign a value of one primitive data type to another type.
In Java, there are two types of casting:
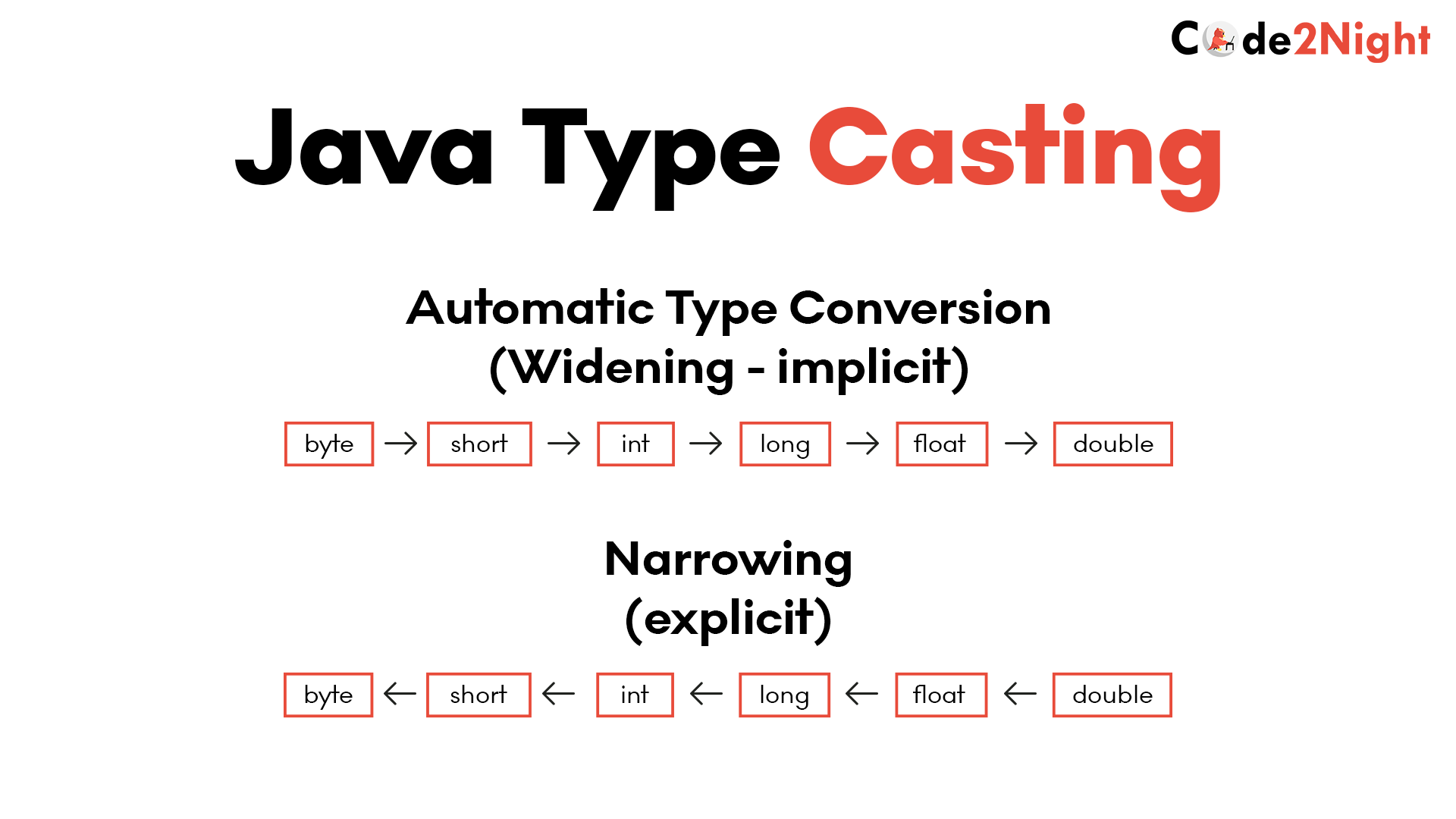
- Widening Casting (automatically) - converting a smaller type to a larger type size
byte->short->char->int->long->float->double - Narrowing Casting (manually) - converting a larger type to a smaller size type
double->float->long->int->char->short->byte
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int myInt = 9;
double myDouble = myInt; // Automatic casting: int to double
System.out.println(myInt); // Outputs 9
System.out.println(myDouble); // Outputs 9.0
}
}Narrowing Casting
Narrowing casting must be done manually by placing the type in parentheses in front of the value:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double myDouble = 9.78d;
int myInt = (int) myDouble; // Manual casting: double to int
System.out.println(myDouble); // Outputs 9.78
System.out.println(myInt); // Outputs 9
}
}